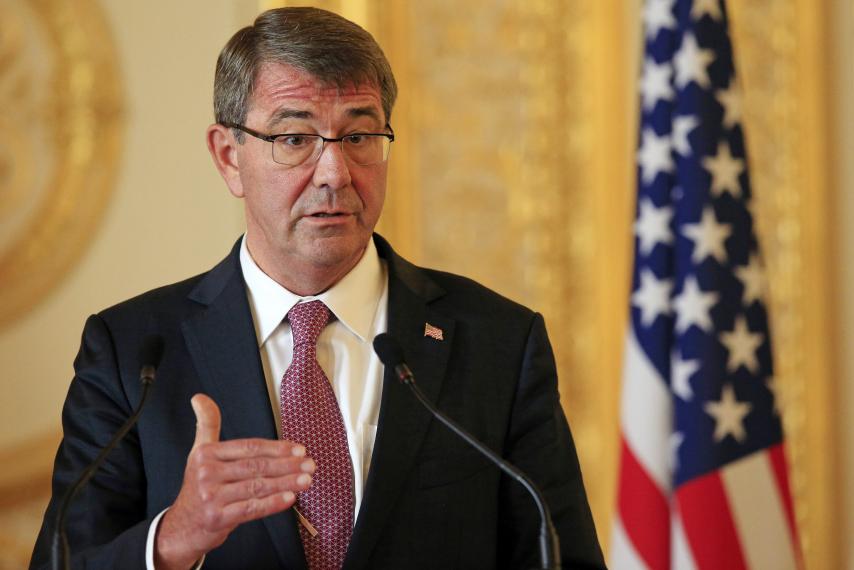
Secretary of Defense Ashton Carter came out against supporting encryption back-doors at a conference panel on Wednesday.
At the RSA information security conference in San Francisco, Carter told a packed room that he supported strong encryption and thought back-door access to encrypted communication as unrealistic. During his talk on the Apple vs. FBI case, which he shied away from the details because it is a “law enforcement issue,” Carter received scattered applause from the crowd of security professionals after he said he supports strong encryption.
“I think first of all that for the Department of Defense, data security including encryption is absolutely essential to us. We are for strong encryption,” Carter says. “I’m not a believer in backdoors or a single technical approach. I don’t think it’s realistic.”
Carter joined Attorney General Loretta Lynch in supporting encryption at the RSA Conference this week. In a stage interview with Bloomberg at the Moscone Center on Tuesday, Lynch called for “a middle ground” between national security and privacy.
In the 50-odd minute talk with Ted Schlein, general partner for the influential venture capital firm Kleiner, Perkins, Caufield & Byers, Carter focused his talk on how to bridge the gap between the Pentagon and Silicon Valley.
Carter, who was appointed to the secretary position last February by President Barack Obama, spoke about two initiatives in particular: the Defense Innovation Unit-Experimental (DIUx) and the Defense Innovation Advisory Board. Both serve to make the department more agile and tech-savvy in the age of cyberwarfare with competitors like Russia and China, Carter says.
“DIUX is a place to connect. It is down the road [from Silicon Valley]. I’ve given it a very open charter,” Carter says. “We need to be very hawkish on the idea of reform.”
Earlier on Wednesday, the Defense Department announced that former Google CEO Eric Schmidt will chair the Defense Innovation Advisory Board. “There is going to be some technical minds who come in and giving me advice to be more innovative,” Carter says. “I am so grateful to Eric Schmidt for his willingness to do this. He’s the perfect chairman for this.”
He also announced a new competition called “Hack the Pentagon” where ethical, or white hat, hackers find vulnerabilities in the Pentagon’s systems and boost the overall cybersecurity of the department. “You would rather find the vulnerabilities in your networks that way than the other way of pilfering information,” Carter says. Hackers must be American citizens, Carter added.
While the Pentagon is bolstering its defenses in protecting its own data, it is also aggressively attacking ISIS, Carter says. Similar to the radio-jamming tactics during the Cold War, the Pentagon has been disrupting the terrorist group’s online channels of communications. “We will and must defeat ISIL. I’m looking for all the ways to accelerate that,” Carter says. “We are using cyber to disrupt communication and doubt the reliability of the comm. Now that enemies use cyber, that’s another way to shut them down.”